Reversible hydrogen electrode
A reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) is a reference electrode, more specific a subtype of the standard hydrogen electrodes for electrochemical processes and differs from the standard hydrogen electrode by the fact that the measured potential does not change with the pH so that they can be directly used in the electrolyte[1][2][3].
The name refers to the fact that the electrode is in the actual electrolyte solution and not separated by a salt bridge. The hydrogen ion concentration is therefore not 1, but corresponds to that of the electrolyte solution; in this way we can achieve a stable potential with a changing pH value. The potential of the RHE correlates to the pH value:
In general, for hydrogen electrodes in which the reaction:
expires, the following dependence of the equilibrium potential 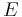 , hydrogen pressure
, hydrogen pressure ![p\mathrm{[H_2]}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/36bd5cc52f63114aeb919c80f1ad1a22.png) and the activity of a
and the activity of a ![a\mathrm{[H_3 O^%2B]}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/d62d7512852d12ca73a255fc57ecd13e.png) of the hydronium ions:
of the hydronium ions:
Here 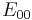 is the standard reduction potential (this is by definition equal to zero), R is the universal gas constant, T the absolute temperature and F is the Faraday constant.
is the standard reduction potential (this is by definition equal to zero), R is the universal gas constant, T the absolute temperature and F is the Faraday constant.
Surges occur in the electrolysis of water which means that the required cell voltage due to kinetic inhibition higher is than the equilibrium potential. The voltage increases with increasing current density at the electrodes. The measurement of equilibrium potentials is therefore possible without power.
Principle
The reversible hydrogen electrode is a fairly practical and reproducible electrode "standard." The term refers to a hydrogen electrode immersed in the electrolyte solution actually used.
The benefit of that electrode is that no salt bridge is needed:
- no contamination of the electrolyte by Cl- or SO42-
- no diffusion potentials at the electrolyte bridge (liquid junction potential). This is important at temperature different to 25 °C.
- long time measurements possible (no electrolyte bridge means no maintenance of the bridge)
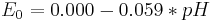
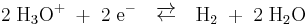
![E = E_{00} %2B \frac{R\;T}{F} \left( \ln \left( a[\mathrm{H_3 O^%2B}] \right) - \frac{1}{2}\ln\left( \;p[\mathrm{H_2}] \right) \right)](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/e4b602e6caf537e97c6224d103802e50.png)